Affine Equivariant Networks Based on Differential Invariants
Abstract
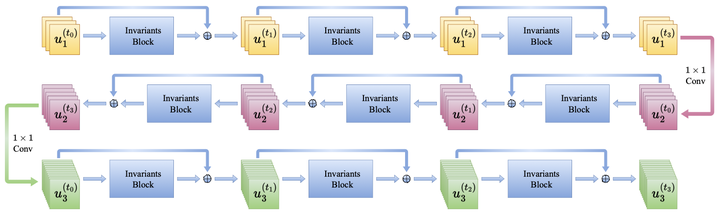
Convolutional neural networks benefit from translation equivariance, achieving tremendous success. Equivariant networks further extend this property to other transformation groups. However, most existing methods require discretization or sampling of groups, leading to increased model sizes for larger groups, such as the affine group. In this paper, we build affine equivariant networks based on differential invariants from the viewpoint of symmetric PDEs, without discretizing or sampling the group. To address the division-by-zero issue arising from fractional differential invariants of the affine group, we construct a new kind of affine invariants by normalizing polynomial relative differential invariants to replace classical differential invariants. For further flexibility, we design an equivariant layer, which can be directly integrated into convolutional networks of various architectures. Moreover, our framework for the affine group is also applicable to its continuous subgroups. We implement equivariant networks for the scale group, the rotation-scale group, and the affine group. Numerical experiments demonstrate the outstanding performance of our framework across classification tasks involving transformations of these groups. Remarkably, under the out-of-distribution setting, our model achieves a 3.37% improvement in accuracy over the main counterpart affConv on the affNIST dataset.